Connecting to a SunSpec Device¶
It is often helpful to quickly visualize, read, and write SunSpec Modbus holding registers. This functionality allows:
- Software developers a quick way to evaluate the SunSpec implementation
- Power electronics engineers the ability to configure the equipment
- DER operators write access to the Modbus server and device measurement feedback
- Testing laboratories can quickly check on the state of the equipment and make appropriate modifications the device
Connection Types¶
There are three types of SunSpec-compliant equipment that can be accessed with LabTest Plus:
- Modbus RTU - A Modbus device connected to the computer using a serial connection.
- Modbus TCP - A Modbus device connected to the computer via a local area network.
- Modbus File - A virtual or cloned device represented by a json file.
Connecting to a Device¶
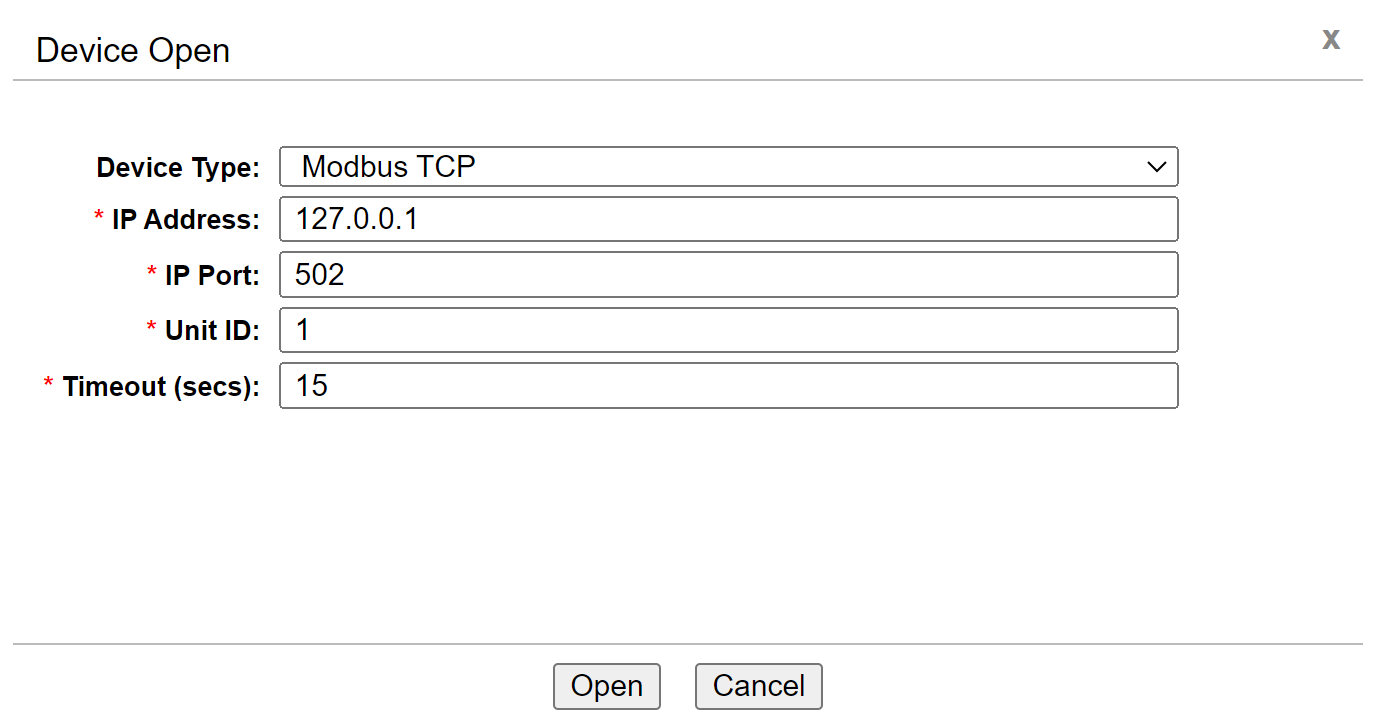
To connect to the equipment, click Device → Open and select the type of device that you would like to connect to from the menu, and enter the following information:
- Modbus TCP
- IP Address - Device IP address
- IP Port - The IP port for the Modbus server, typically 502
- Unit ID - The Modbus ID
- Timeout (secs) - Connection timeout in seconds
- Modbus RTU
- Interface Name - Windows serial communication port, e.g., COM0
- Unit ID - The Modbus ID
- Baud Rate - Serial communication port baud rate. Options include 9600, 19200, 115200, etc.
- Parity - Serial communication port parity
- Timeout (secs) - Connection timeout in seconds
- Device File
- File Name - Path to the device information model json file. These files can be generated using the Device → Export As functionality included in SunSpec Dashboard.
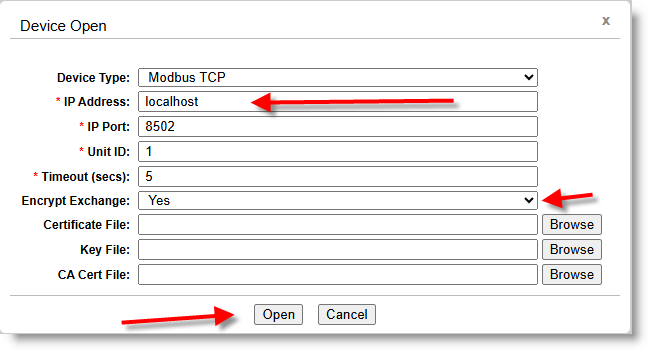
- To activate Encrypted Exchange, make sure IP Address is localhost, leave Certificate File, Key File and CA Cert File rows blank and click Open.
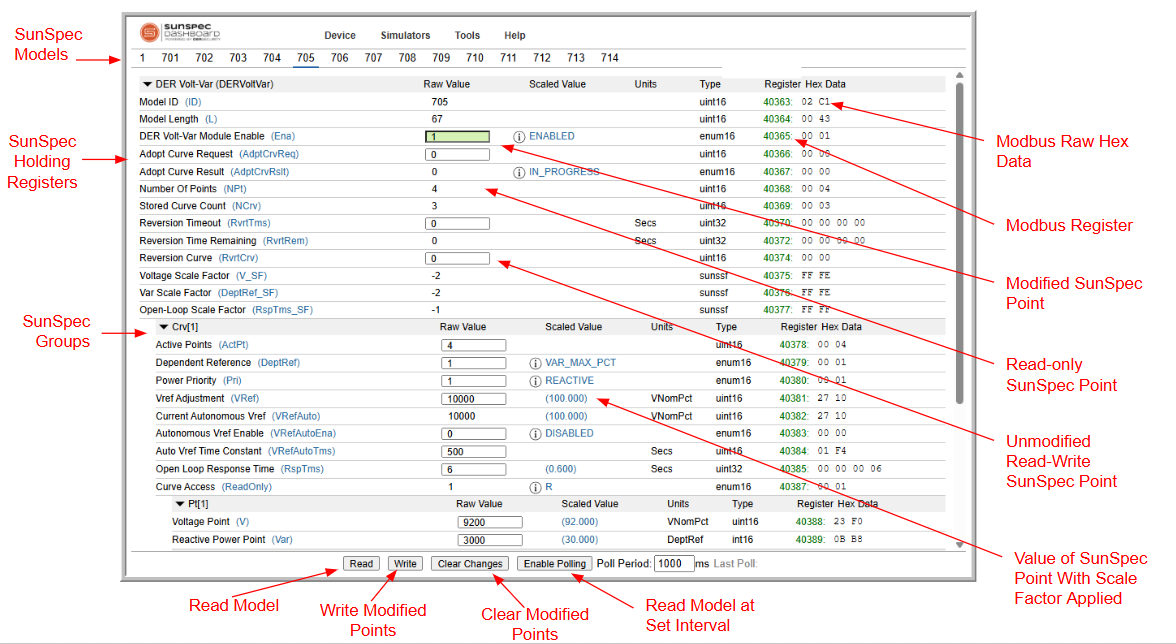
Interacting with a Device¶
Once a device is connected, it is possible to:
- Inspect the supported SunSpec models and supported SunSpec points.
- Read the SunSpec models or poll the registers at a set interval.
- Write Modbus registers to change the operation of the equipment.
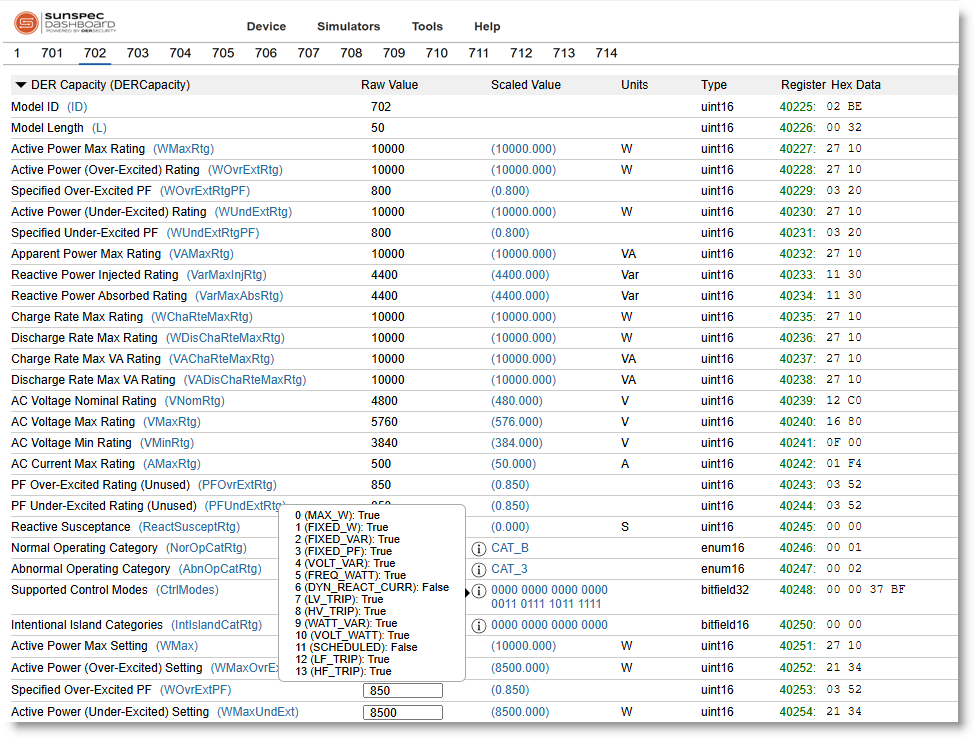
The model 701 (DERMeasureAC)¶
The model 701 (DERMeasureAC) lists the monitoring information of the DER.
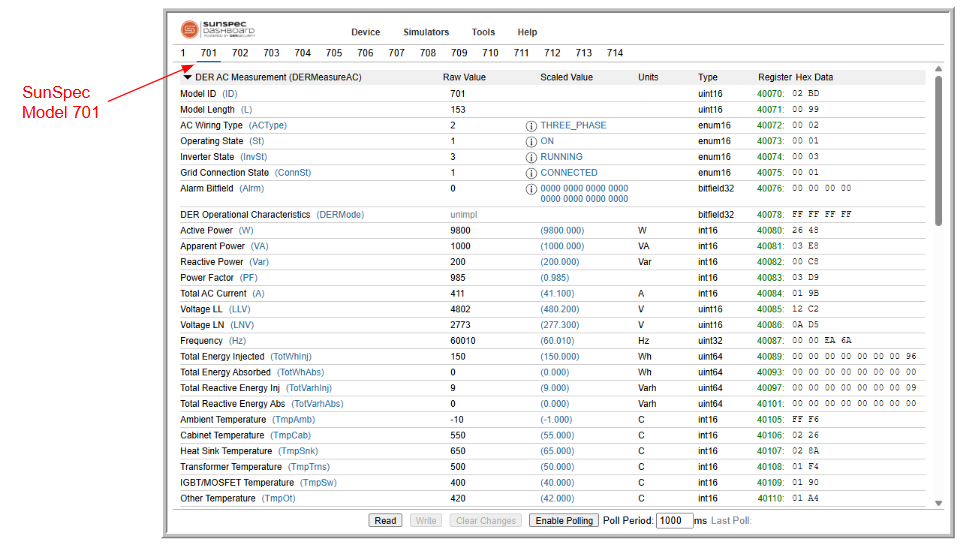
- This model presents the current operating state of the DER.
- This information may only be read.
- The model consists of registers that provide the summary of the system as well as per phase details.
- For detailed information, please check the SunSpec Modbus Model Reference Sheet